Note: This post is still underconstruction.
You can view observables as the 2.0 version of Promise. The big gain in using observables is that you can have a stream of information instead of the one return value of a promise.
Map
Map return a new stream based on the inital stream, it does not modify the original stream in any way. With this immutablility we allow chaining of functions. The map(f) function replaces each emitted value according to a function f you provide.
initialStream: ---c----c--c----c------c-->
vvvvv map(c becomes 1) vvvv
endStream: ---1----1--1----1------1-->
Scan
This function aggregates all previous values on the stream, producing value x = g(accumulated, current), where g is simply the add function. The counterStream emits the total number of clicks.
initialStream: ---1----1--1----1------1-->
vvvvvvvvv scan(+) vvvvvvvvv
endStream: ---1----2--3----4------5-->
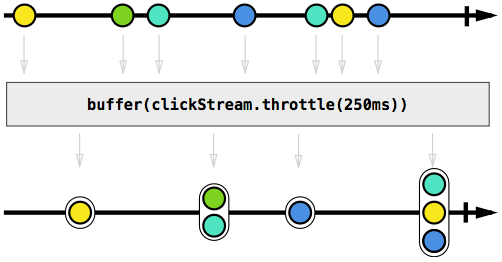
Buffer
This method periodically gathers emitted items. We can either give only a bufferClosingSelector or add a bufferOpenings as well.
Filter
This does exactly what you think it does, it filters the stream output based on your given criteria.
initialStream: ---1----3--1----7------4-->
vvvvvv filter(x > 2) vvvvvv
endStream: --------3-------7------4-->
Merge
With this function you can easily merge multiple stream into one stream.
stream A: ---a--------e-----o----->
stream B: -----B---C-----D-------->
vvvvvvvvv merge vvvvvvvvv
endStream: ---a-B---C--e--D--o----->
StartWith
No matter what your input stream looks like, the output stream will always have x at the beginning.
stream A: ----a--------e-----o----->
vvvv startsWith(null) vvv
endStream: -N--a--------e-----o----->
CombineLatest
It takes stream A and B as inputs and whenever either stream emits a value, combineLatest joins the two most recently emitted values a and b from both streams and outputs a value c = f(x,y).
stream A: --a-----------e--------i-------->
stream B: -----b----c--------d-------q---->
vvvvvvvv combineLatest(f) vvvvvvv
endStream: ----AB---AC--EC---ED--ID--IQ---->
Concat
Use this operator when the order is important, for example when you need to send HTTP requests that should be in order.
stream A: --a---------->
stream B: -----b-------c---->
vvvvvvvvvv concat(A,B) vvvvvvvvvv
endStream: ----A--------------B-------C---->
Forkjoin
Equivalent of Promise.all(), give back all the values when all the streams are completed.
stream A: --a---------->
stream B: -----b-----c->
vvvvvvvvv forkjoin(A,B) vvvvvvvvv
endStream: ----------------------------[A,B,C]->
Pairwise
Gets the emitted value but also includes the previous value.
stream A: --a----b-------c---d----e---f---->
vvvvvvvvvv pairwise(f) vvvvvvvvvv
endStream: --NA---AB------BC--CD---DE--EF--->